-
Your concerns
Our articles to help you gain a better understanding
-
Our solutions
-
Ducray Dermatological laboratories
Our articles to help you gain a better understanding
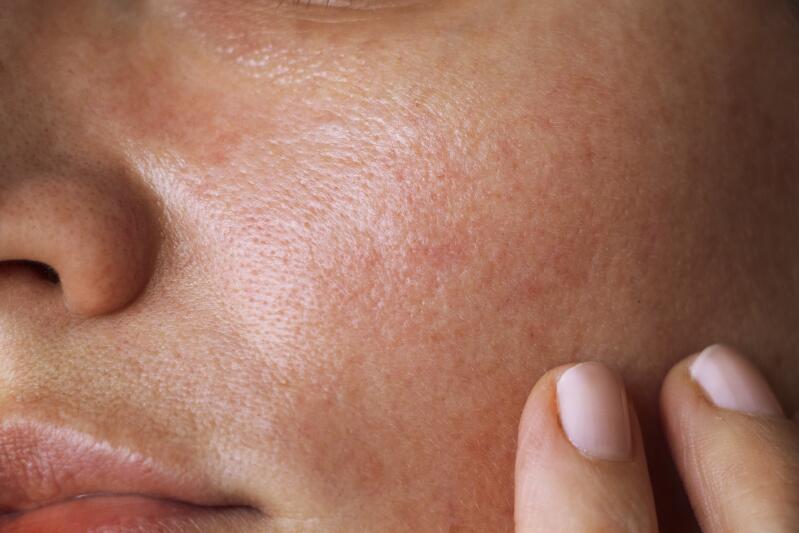
One of the main features of acne is hyperseborrhea, i.e. the overproduction of sebum. This excess sebum makes the skin oily, shiny and prone to spots.

Summary
Sebum is a physiological secretion of the sebaceous glands that are found, for example, in the T-zone of the face (forehead, nose and cheeks, chin), the chest, and the back. It is a fatty substance that protects the skin. Sebum combines with sweat to form the hydrolipidic film, which is key to preventing the evaporation of water present in the skin and fighting against dry skin.
The sebaceous glands are dependent on hormones called androgens. In certain periods of life, particularly during puberty, these androgens, present in greater quantities, spark the growth of the sebaceous glands and sebum production. Excess sebum and/or lower quality sebum makes the skin oily, prevents dead cells from being eliminated properly and provides a culture medium for the development of pro-inflammatory acne bacteria. Excess sebum becomes one of the main causes of acne, causing blackheads, whiteheads and inflammatory spots.
Certain anti-sebum treatments should be avoided: in particular, it is not worthwhile changing your diet to remove all fats. This will not prevent the build-up of excess sebum and, conversely, it can lead to deficiencies. It is also counterproductive to try to dry out your skin, for instance through overly aggressive soaps, as the skin then reacts by producing even more sebum. The ideal way to combat excess sebum is to use a gentle, soap-free cleansing product, a mattifying care product, or even a lotion or mask to strengthen purifying and anti-shine action.
Oily or acne-prone skin

Oily or acne-prone skin
NEWSLETTER
Dermatological expertise
To better understand your skin and hair, discover our exclusive content and innovative care products designed to improve your quality of life..