-
Your concerns
Our articles to help you gain a better understanding
-
Our solutions
-
Ducray Dermatological laboratories

The hair growth cycle follows a very precise pattern, divided into three phases: a growth phase (anagen), a regression phase (catagen) and a shedding phase (telogen). However, it can get stuck and that's when hair loss occurs. Depending on the type of hair loss, the hair cycle is modified differently. What are the different symptoms of alopecia?

Summary
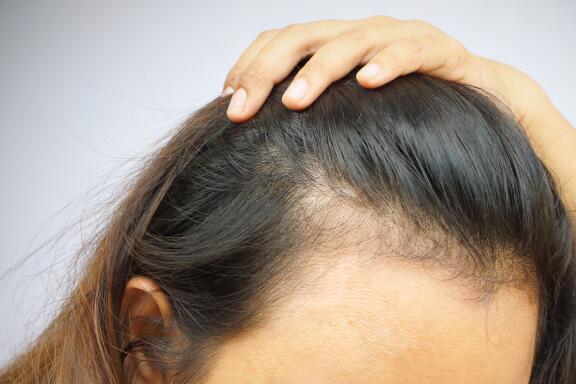
Also known as occasional hair loss or, in medical language, acute telogen effluvium. There are different types of reactional hair loss which can occur at any time depending on fatigue, stress, season, climate, eating habits or hormonal balance. This type of hair loss is sudden, some people can even have hair falling out by the handful, and lasts less than 6 months. Alopecia is defined as diffuse, i.e., evenly distributed throughout the head. When the triggering factor has been identified and eliminated, improvement is always seen, although it can take between 12 and 18 months for the hair to return to its original state.
In this case, the mechanism is hormonal and hereditary. It is not uncommon for this form of hair loss to lead to baldness in men. It is even the most common form of alopecia in men: 70% to 80% are affected in their lifetime*. Its symptoms: progressive hair loss as the years go by, characterized by thin hair and localized hair loss on the top of the head. Note that female androgenetic alopecia is not uncommon either. In this case, it rarely leads to baldness, but it is responsible for a, sometimes significant, loss of hair volume and density.
This other type of chronic hair loss fluctuates and lasts for more than 6 months. This type of hair loss generally occurs in women between 30 and 50 years old with, originally, healthy, thick and shiny hair. Among its causes: thyroid disorders, anorexia, iron deficiency and certain medications. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, chronic hair loss does not result in permanent or irreversible hair loss. Symptoms to be aware of: diffuse, somewhat light hair loss, but which lasts for more than 6 months and which can lead to a progressive reduction in hair mass.
This type of hair loss corresponds to a sudden shedding of the hair fiber during its growth phase after multiplication of the cells of the hair follicle is stopped. Its onset is quick, on the order of a few days to a few weeks. It appears as diffuse alopecia, which can affect the entire scalp. This type of hair loss is mainly observed following cancer chemotherapy or exposure of the head and neck to radiotherapy. It can also affect the eyebrows and body hair.
It is called androgenetic alopecia because it is truly hereditary. Baldness is the most common form of androgenetic alopecia in men. The excessive presence of male hormones (androgens, including testosterone), modifies the natural hair cycle by accelerating its growth rate. This action wears out the hair cycles faster than expected: hair becomes thinner and thinner, miniaturizing into light downy hair until it stops growing and disappears permanently. We generally observe localized alopecia on certain areas, on the forehead and the top of the skull.
This chronic and diffuse type of hair loss appears gradually. It usually begins just after puberty and develops gradually to settle in between the ages of 30 and 40. The symptoms of this type of alopecia: light but progressive hair loss on the top of the head, dull and often greasy hair. In some cases, we see hair loss with itchy scalp.
Hair loss by the handful, thin hair, diffuse loss of hair volume... These are the most common symptoms, those that can be a sign of temporary or more severe hair loss. More than the hair loss itself, the time in the patient’s life when it appears is important. Analyzing daily habits and the events of the last few months often allows us to identify the cause more easily. Stress, anxiety, being overworked, experiencing an emotional shock: these elements can have an impact on the quality and beauty of your hair.
In each of the cases mentioned above, in order to analyze the symptoms of your hair loss in the best possible way, consult your pharmacist, your doctor and/or a dermatologist, a hair and scalp specialist, as soon as the first signs appear. While not all types of hair loss require medicinal treatment, the main objective is to identify the type of hair loss and its cause in order to manage it as effectively as possible. Hair loss is a frequent reason for consultation in dermatology.
Take your diagnostic test online.
* Source: Blume-Peytavi et al., 2011; Norwood, 1975**Source: Grover and Khurana, 2013