-
Your concerns
Our articles to help you gain a better understanding
-
Our solutions
All our products
- Hair loss – ANAPHASE+, CREASTIM, NEOPTIDE, ANACAPS
- Hyperpigmentation - MELASCREEN
- Itching - SENSINOL
- Normal to delicate hair - EXTRA-GENTLE
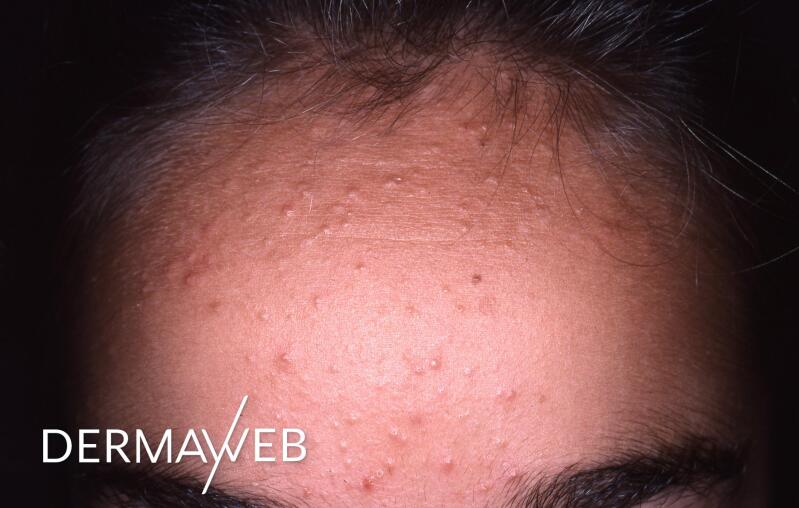
- Oily and acne-prone skin - KERACNYL
- Oily hair – ARGEAL, SABAL
- Photo-aging– MELASCREEN
- Skin prone to seborrheic dermatitis – KELUAL DS
- Psoriasis-prone skin - KERTYOL PSO
-
DUCRAY Dermatological Laboratories